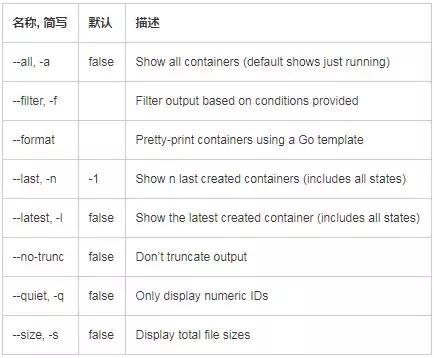
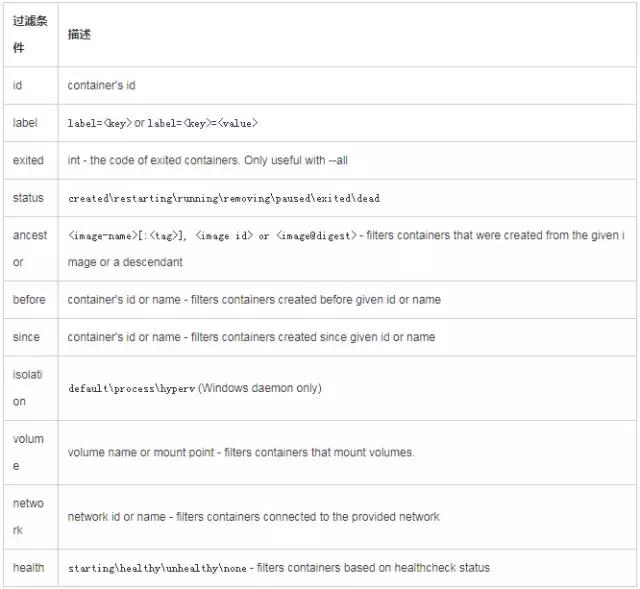
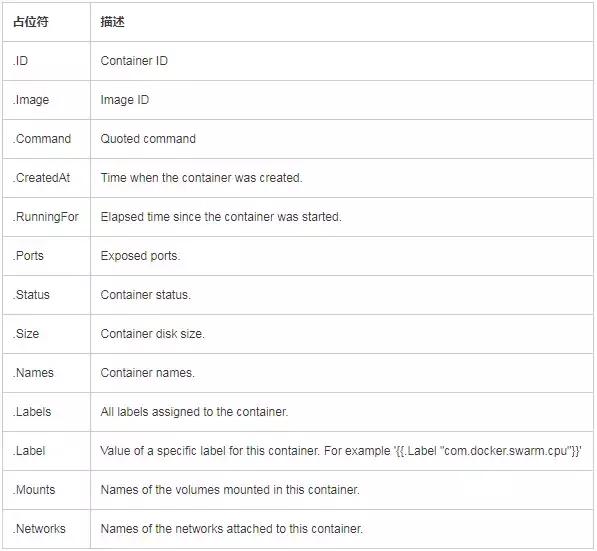
1.登录gitbash命令端进入本地git库目录
Administrator@PC201601200946 MINGW32 /d/gitrespository/crmweb (master)
2.创建.gitignore

3.修改文件,添加忽略正则

.idea //忽略.idea文件夹及文件夹下文件
*.iml //忽略以.iml结尾的文件
【例子】
# 忽略*.o和*.a文件
*.[oa]
# 忽略*.b和*.B文件,my.b除外
*.[bB]
!my.b
# 忽略dbg文件和dbg目录
dbg
# 只忽略dbg目录,不忽略dbg文件
dbg/
# 只忽略dbg文件,不忽略dbg目录
dbg
!dbg/
# 只忽略当前目录下的dbg文件和目录,子目录的dbg不在忽略范围内
/dbg
# 以'#'开始的行,被视为注释.
* ?:代表任意的一个字符
* *:代表任意数目的字符
* {!ab}:必须不是此类型
* {ab,bb,cx}:代表ab,bb,cx中任一类型即可
* [abc]:代表a,b,c中任一字符即可
* [ ^abc]:代表必须不是a,b,c中任一字符
4.提交本地版本库,推送到远程项目,方便协作,项目管理

添加忽略之后,已经提交到版本库中的文件是无法忽略的。只能clone到本地,删除后,再进行忽略。
.gitignore只能忽略那些原来没有被track的文件,如果某些文件已经被纳入了版本管理中,则修改.gitignore是无效的。
正确的做法是在每个clone下来的仓库中手动设置不要检查特定文件的更改情况。
git update-index –assume-unchanged PATH 在PATH处输入要忽略的文件。
另外 git 还提供了另一种 exclude 的方式来做同样的事情,不同的是 .gitignore 这个文件本身会提交到版本库中去。用来保存的是公共的需要排除的文件。而 .git/info/exclude 这里设置的则是你自己本地需要排除的文件。 他不会影响到其他人。也不会提交到版本库中去
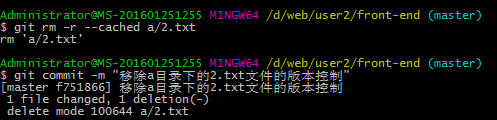
其他操作:git删除远程仓库的文件或目录
git rm -r –cached a/2.txt //删除a目录下的2.txt文件 删除a目录git rm -r –cached a
git commit -m "删除a目录下的2.txt文件"
git push
Note:
用-r参数删除目录, git rm –cached a.txt 删除的是本地仓库中的文件,且本地工作区的文件会保留且不再与远程仓库发生跟踪关系,如果本地仓库中的文件也要删除则用git rm a.txt